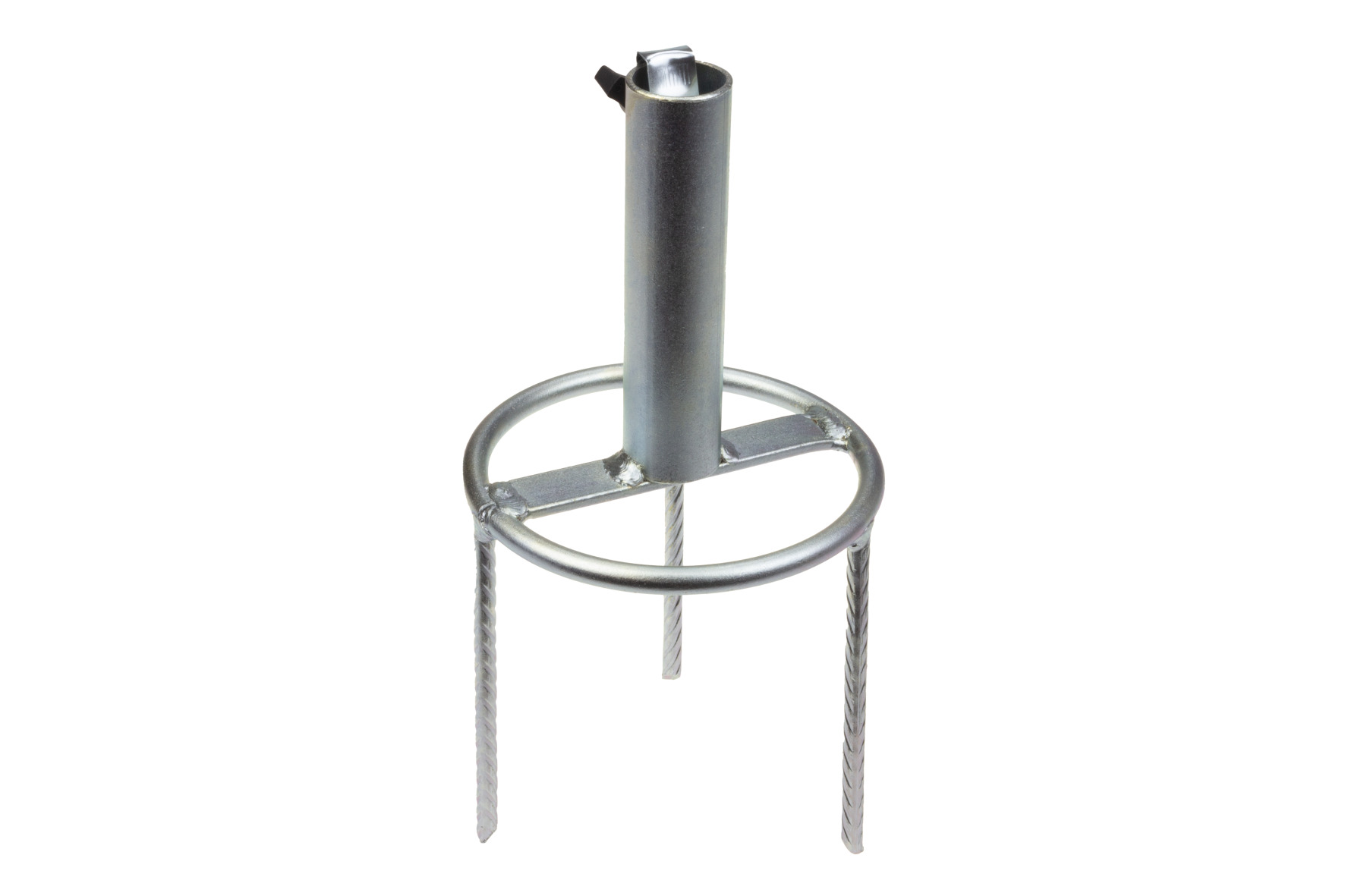
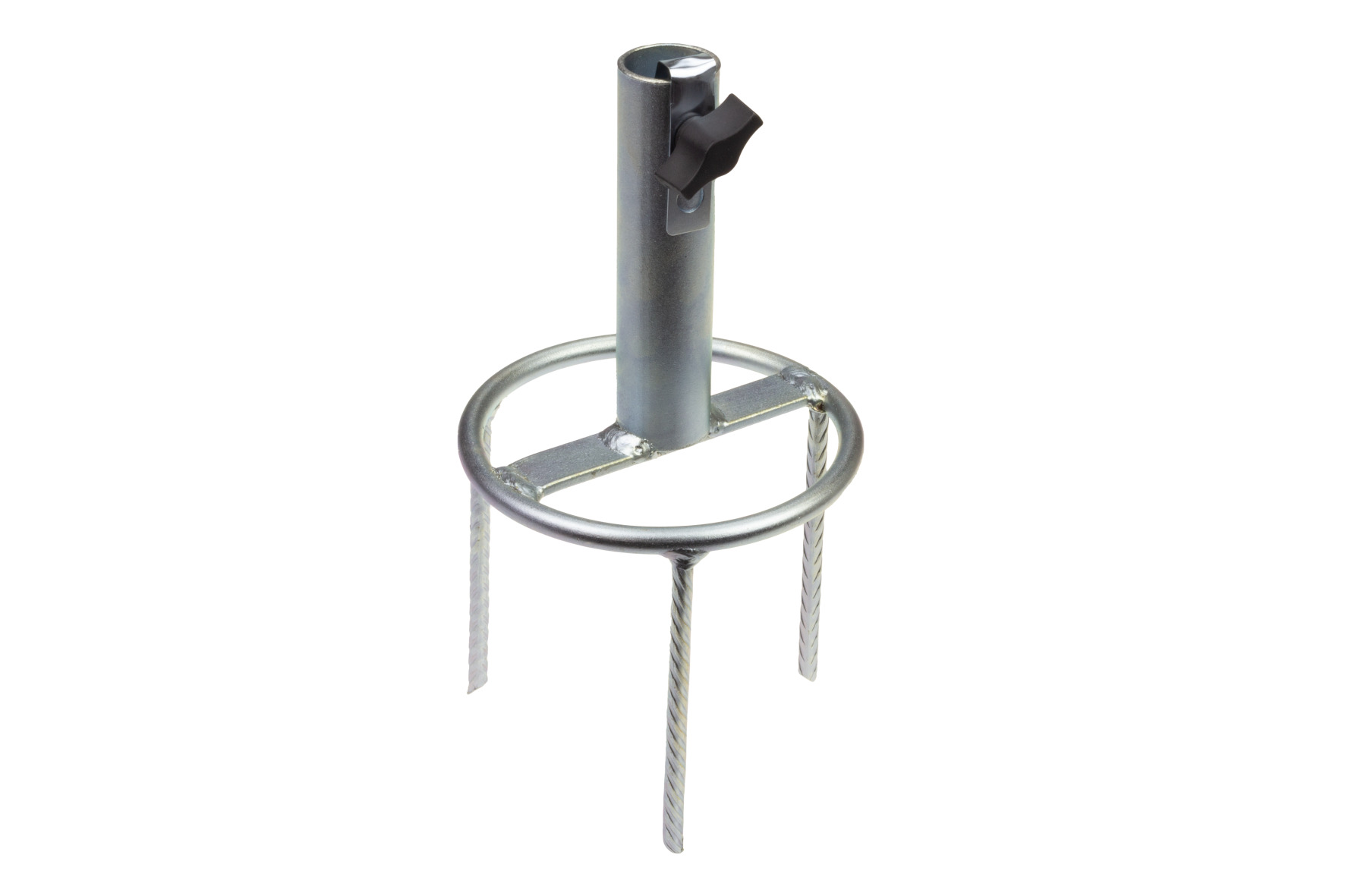
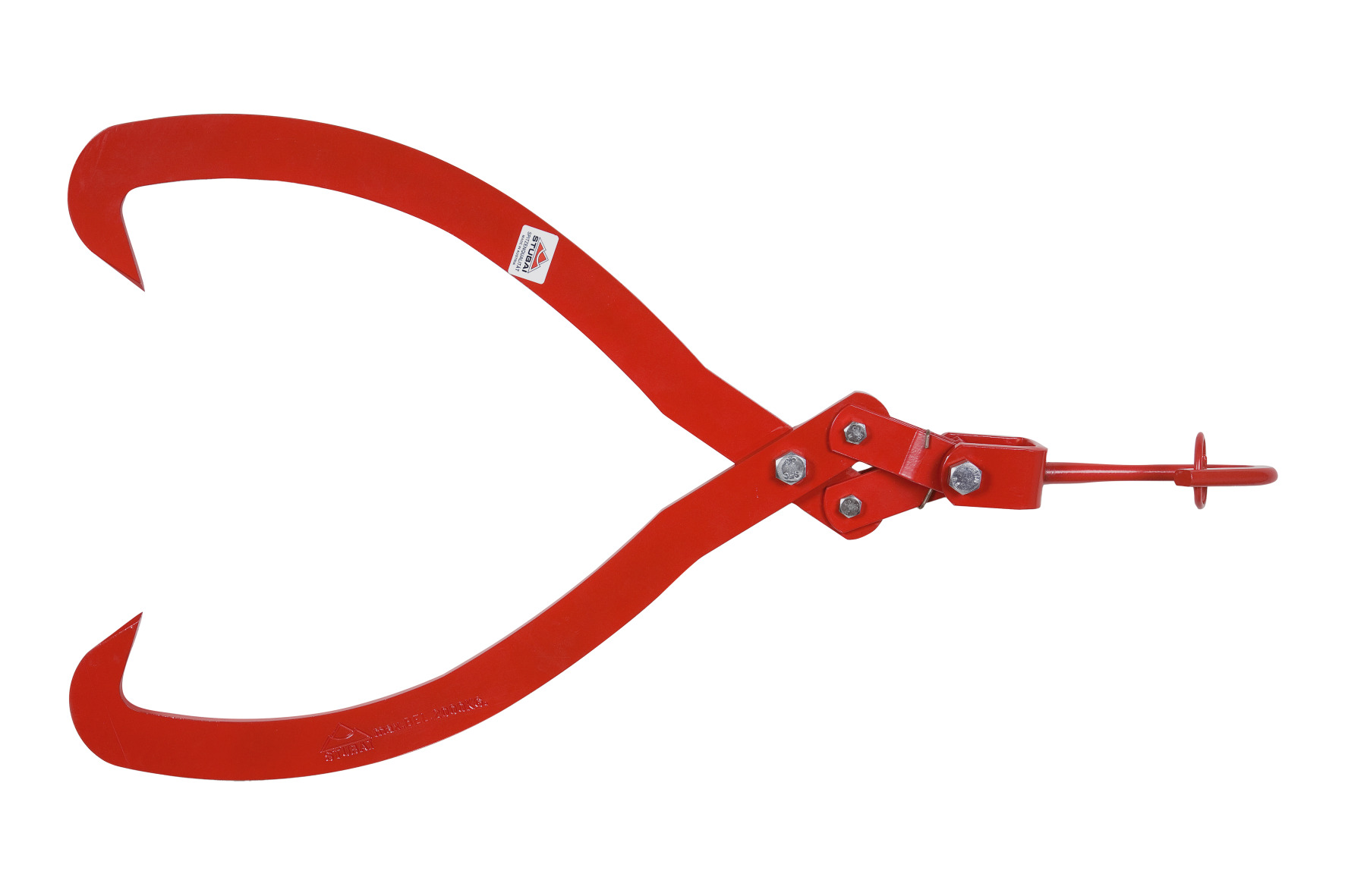
8650 Umbrella stand
The STUBAI umbrella stands have the advantage that they are very easy to insert into the lawn and no stone or other tool is required to hammer them in, which would only lead to damage. In addition, they also serve as lawn aeration as soon as the location is changed.
| Item No | Designation | Weight | Height | Opening |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 865001 | Umbrella stand 25 mm | 600 g | 150 mm | 25 mm |
| 865002 | Umbrella stand 25 mm | 1000 g | 200 mm | 25 mm |
| 865003 | Umbrella stand 38 mm | 1450 g | 250 mm | 28 mm |
| 865004 | Umbrella stand 50 mm | 2500 g | 300 mm | 50 mm |
Manufacturer information (GPSR)
MANUFACTURER ACCORDING TO THE EU GENERAL PRODUCT SAFETY REGULATION (GPSR)
STUBAI ZMV GmbH
Dr. Kofler Straße 1
A-6166 Fulpmes
Phone: +43 5225 6960 211
Email: office@stubai.com
Safety Instructions for Forestry Tools
General Information:
• Certain forestry tools are KWF certified.
• Use according to application: Use each forestry tool only for its intended purpose. Forestry tools such as axes, log hooks or lifting levers are specifically designed for working with wood and not for other materials.
• Proper handling: Always hold tools by their designated handles to ensure safe and precise operation. Avoid touching the working surfaces of the tools, especially sharp or hard edges.
• Avoid overloading: Do not overload tools with excessive force or overly heavy objects to prevent breakage or malfunction. Each tool has specific load limits that must not be exceeded.
• Forestry tools may only be used by persons with limited physical, sensory or mental abilities, or lacking experience and/or knowledge, if they are supervised by a person responsible for their safety, have received instructions on how to use forestry tools, and have understood the resulting hazards.
• Children may only use forestry tools if they are over 8 years old and are supervised by a person responsible for their safety, have received instructions on how to use forestry tools, and have understood the resulting hazards.
• Keep packaging films away from children; risk of suffocation!
Intended Use:
• Safety is only ensured when the tool is used as intended. Use forestry tools exclusively for their designated purpose. Incorrect use may lead to tool breakage and injuries.
Improper Use:
• Use as a hammer or on surfaces that are not made of wood is not permitted.
Inspection Before Use:
• Ensure integrity: Check forestry tools before each use for damage such as cracks, loose parts or rust.
• Do not use damaged forestry tools: Defective forestry tools must not be used and must be taken out of service immediately.
Personal Protective Equipment:
• Wear safety goggles: Use safety goggles to protect yourself from chipping material.
• Hand protection: Wear robust work gloves that provide a secure grip and protect against splinters or skin injuries.
• Safety footwear: Wear safety shoes with a metal or plastic toe cap to protect your toes.
Specific Instructions for Forestry Tools:
• Axe:
o Ensure that the blade of the axe is sharp and free from damage, as a dull blade increases the risk of slipping and injury.
o Avoid using the axe blade on hard materials or for purposes other than cutting wood.
o Always maintain sufficient distance from other people and avoid working in confined spaces.
• Billhook:
o Check the tip of the billhook for wear or damage. A damaged tip can result in uneven cutting and may endanger the tool itself.
o Ensure that the handle of the billhook fits securely in your hand to prevent slipping. A slippery handle increases the risk of injury.
• Log tongs:
o Ensure that the jaws of the log tongs grip properly and do not loosen or bend. Loose or damaged tongs can cause the workpiece to slip and move uncontrollably.
o Make sure the handle of the tongs is in perfect condition to prevent slipping or breaking during use.
• Skidding tongs:
o Regularly check the joints and connections of the skidding tongs for wear or damage. A loose connection can impair functionality and increase the risk of accidents.
o Avoid using skidding tongs for excessive loads. They are designed for pulling logs but should not be used for objects that are too large or heavy.
• Log hook:
o Ensure that the hook of the log hook is sharp and undamaged. A dull or damaged hook cannot grip wood properly and may cause slipping.
o Insert the log hook correctly into the wood structure to ensure precise and safe handling.
o Always wear safety goggles and gloves when working with log hooks to protect yourself from sharp edges and wood splinters.
• Lifting lever:
o Ensure that the lifting lever is firmly and securely positioned on the tree trunk to guarantee a safe lifting and levering mechanism. A loose lever cannot move the trunk safely and may cause uncontrolled tipping or falling.
o Check the edges of the lifting lever for sharp edges or wear that could increase the risk of slipping and injury.
o Use the lifting lever only in stable, controlled environments to prevent unexpected tipping of the trunk.
Maintenance, Care and Storage:
• Regular inspection: Check forestry tools regularly for wear, cracks or loose handles. A damaged forestry tool can cause serious injuries.
• Cleaning after use: Clean all forestry tools thoroughly after each use to remove dirt, resin or other residues that may impair functionality.
• Sharpening: Sharpen blades regularly to ensure precise and safe work. A dull tool increases the risk of slipping and unwanted movements.
• Storage: Store tools out of reach of children and persons with limited physical, sensory or mental abilities, in a safe, dry place such as a toolbox or tool wall to prevent accidents and damage.
Special Notes:
• Avoid improvisation: Use forestry tools only for their intended applications. Using them for unsuitable tasks may damage the tools or workpieces and lead to accidents.
• Transport: Ensure that forestry tools are securely fastened during transport and that sharp edges are protected to avoid injuries.
This text has been partially translated with the support of AI technology.
STUBAI ZMV GmbH
Dr. Kofler Straße 1
A-6166 Fulpmes
Phone: +43 5225 6960 211
Email: office@stubai.com
Safety Instructions for Forestry Tools
General Information:
• Certain forestry tools are KWF certified.
• Use according to application: Use each forestry tool only for its intended purpose. Forestry tools such as axes, log hooks or lifting levers are specifically designed for working with wood and not for other materials.
• Proper handling: Always hold tools by their designated handles to ensure safe and precise operation. Avoid touching the working surfaces of the tools, especially sharp or hard edges.
• Avoid overloading: Do not overload tools with excessive force or overly heavy objects to prevent breakage or malfunction. Each tool has specific load limits that must not be exceeded.
• Forestry tools may only be used by persons with limited physical, sensory or mental abilities, or lacking experience and/or knowledge, if they are supervised by a person responsible for their safety, have received instructions on how to use forestry tools, and have understood the resulting hazards.
• Children may only use forestry tools if they are over 8 years old and are supervised by a person responsible for their safety, have received instructions on how to use forestry tools, and have understood the resulting hazards.
• Keep packaging films away from children; risk of suffocation!
Intended Use:
• Safety is only ensured when the tool is used as intended. Use forestry tools exclusively for their designated purpose. Incorrect use may lead to tool breakage and injuries.
Improper Use:
• Use as a hammer or on surfaces that are not made of wood is not permitted.
Inspection Before Use:
• Ensure integrity: Check forestry tools before each use for damage such as cracks, loose parts or rust.
• Do not use damaged forestry tools: Defective forestry tools must not be used and must be taken out of service immediately.
Personal Protective Equipment:
• Wear safety goggles: Use safety goggles to protect yourself from chipping material.
• Hand protection: Wear robust work gloves that provide a secure grip and protect against splinters or skin injuries.
• Safety footwear: Wear safety shoes with a metal or plastic toe cap to protect your toes.
Specific Instructions for Forestry Tools:
• Axe:
o Ensure that the blade of the axe is sharp and free from damage, as a dull blade increases the risk of slipping and injury.
o Avoid using the axe blade on hard materials or for purposes other than cutting wood.
o Always maintain sufficient distance from other people and avoid working in confined spaces.
• Billhook:
o Check the tip of the billhook for wear or damage. A damaged tip can result in uneven cutting and may endanger the tool itself.
o Ensure that the handle of the billhook fits securely in your hand to prevent slipping. A slippery handle increases the risk of injury.
• Log tongs:
o Ensure that the jaws of the log tongs grip properly and do not loosen or bend. Loose or damaged tongs can cause the workpiece to slip and move uncontrollably.
o Make sure the handle of the tongs is in perfect condition to prevent slipping or breaking during use.
• Skidding tongs:
o Regularly check the joints and connections of the skidding tongs for wear or damage. A loose connection can impair functionality and increase the risk of accidents.
o Avoid using skidding tongs for excessive loads. They are designed for pulling logs but should not be used for objects that are too large or heavy.
• Log hook:
o Ensure that the hook of the log hook is sharp and undamaged. A dull or damaged hook cannot grip wood properly and may cause slipping.
o Insert the log hook correctly into the wood structure to ensure precise and safe handling.
o Always wear safety goggles and gloves when working with log hooks to protect yourself from sharp edges and wood splinters.
• Lifting lever:
o Ensure that the lifting lever is firmly and securely positioned on the tree trunk to guarantee a safe lifting and levering mechanism. A loose lever cannot move the trunk safely and may cause uncontrolled tipping or falling.
o Check the edges of the lifting lever for sharp edges or wear that could increase the risk of slipping and injury.
o Use the lifting lever only in stable, controlled environments to prevent unexpected tipping of the trunk.
Maintenance, Care and Storage:
• Regular inspection: Check forestry tools regularly for wear, cracks or loose handles. A damaged forestry tool can cause serious injuries.
• Cleaning after use: Clean all forestry tools thoroughly after each use to remove dirt, resin or other residues that may impair functionality.
• Sharpening: Sharpen blades regularly to ensure precise and safe work. A dull tool increases the risk of slipping and unwanted movements.
• Storage: Store tools out of reach of children and persons with limited physical, sensory or mental abilities, in a safe, dry place such as a toolbox or tool wall to prevent accidents and damage.
Special Notes:
• Avoid improvisation: Use forestry tools only for their intended applications. Using them for unsuitable tasks may damage the tools or workpieces and lead to accidents.
• Transport: Ensure that forestry tools are securely fastened during transport and that sharp edges are protected to avoid injuries.
This text has been partially translated with the support of AI technology.